As the popularity of electric vehicles continues to grow, the increased demand highlights the charging challenges owners often face. Charge stations are not widely distributed or available, and all require the driver to connect a cable to the car. However, electrical power, unlike liquid fuels, does not require a physical connection to the car, so as wireless charging technology advances, it will become convenient to charge in many more places without connecting cables. Get ready for wireless charging.
 A wireless charging system consists of fixed and mobile modules. In the case of leading wireless-charging technology company, WiTricity, the fixed part has a wall mounted power converter that changes normal mains electricity (at 50 or 60 Hz) to the much higher frequency of 85 kHz. This high-frequency power is sent to a fixed ground pad mounted on or under the pavement where a copper coil generates a magnetic field. The mobile part is attached to the underside of a car or SUV where another copper coil intersects the magnetic field and, using power electronics, transforms it into DC power to charge the vehicle’s battery. This so called magnetic-resonance-charging technique can achieve grid-to-battery efficiency of up to 94 percent, which is equivalent to a wired connection.
A wireless charging system consists of fixed and mobile modules. In the case of leading wireless-charging technology company, WiTricity, the fixed part has a wall mounted power converter that changes normal mains electricity (at 50 or 60 Hz) to the much higher frequency of 85 kHz. This high-frequency power is sent to a fixed ground pad mounted on or under the pavement where a copper coil generates a magnetic field. The mobile part is attached to the underside of a car or SUV where another copper coil intersects the magnetic field and, using power electronics, transforms it into DC power to charge the vehicle’s battery. This so called magnetic-resonance-charging technique can achieve grid-to-battery efficiency of up to 94 percent, which is equivalent to a wired connection.
The fixed charging pad contains about 20 meters of 5mm diameter copper wire wound into a 65cm x 50cm rectangular coil. The copper wire is unusual: it is made of about 1000 strands of 0.1mm diameter wires woven into a pattern that reduces electrical losses during high-frequency operation. A similar but somewhat smaller coil is affixed to the vehicle.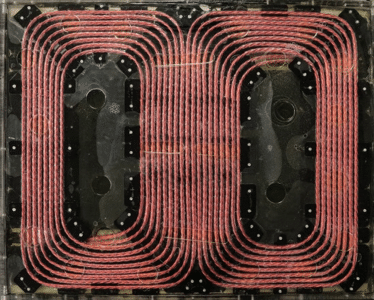
Morris Kesler, chief technology officer of WiTricity, estimates that for a sedan, there is about 1.7 kg of copper in the fixed coil, about 1 kg in the cable from the wall box to the ground pad, and about 1 kg in the vehicle coil. Additional copper is contained in the frequency converting power electronics modules. Overall, wireless charging will require about 4 kg of copper per passenger car.
Standards are critical to making new technology accessible on a wide scale. The SAE-J2954 standard for wireless charging provides the first worldwide specification for wireless power transfer for electric vehicles up to 11 kW power levels. It should be a great benefit to drivers and automakers because it eliminates the conflict among plug-in standards and simplifies charging. Because there is no physical connection between the vehicle and the charger, wireless charging ensures complete interoperability across all vehicle makes. Dedicated chargers for specific vehicle types are not needed. The standard establishes a new method to align vehicles over a charging pad and allows charging even in rain or snow. Combined with communications, it can allow drivers (or driverless autonomous vehicles) to park their vehicles, organize payment, and charge automatically.
 According to WiTricity’s CEO, Alex Gruzen, EV makers indicate that 95 percent or more of all charging requirements are between 7.7 and 11 kW. Higher power systems will be available for commercial customers who operate fleets of trucks or buses. WiTricity is in the process of licensing its technology to companies worldwide.
According to WiTricity’s CEO, Alex Gruzen, EV makers indicate that 95 percent or more of all charging requirements are between 7.7 and 11 kW. Higher power systems will be available for commercial customers who operate fleets of trucks or buses. WiTricity is in the process of licensing its technology to companies worldwide.
Wireless charging is also beneficial for vehicle-to-grid application because the technology and hardware work equally well in either direction, and the car is always connected to the grid if it is parked over a charging hub. In contrast, a car needing to be plugged in can only be connected to the grid when the charging cable is attached.
Wireless charging is an important component in the transition to a future where electric cars are predominant. High-power, high-speed chargers may be necessary for those traveling long distances, but for normal daily driving, the ability to easily top up a battery while shopping, working, or visiting a restaurant is a welcome convenience.

Source: Witricity
Source: New England Wire Technologies
